Json是平时常用的数据结构,对于C++ Native代码来说,选择一个优秀的json解析器对于应用来说十分重要。json_spirit是codeproject上比较热门的json解析器,具有优异的使用接口,以及不错的效率(用了boost::spirit::classic解析框架)。
先简单介绍JSON语法(JavaScript Object Notation)
- “名称/值”对的集合(A collection of name/value pairs),它被理解为对象(object)或字典(dictionary)
- 值的有序列表(An ordered list of values),它被理解为数组(array)
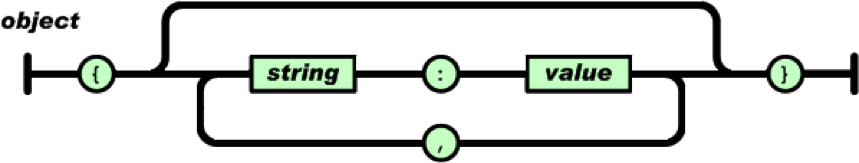
对象
对象是一个无序的“‘名称/值’ 对”集合:
- 一个对象以“{”(左括号)开始,“}”(右括号)结束
- 每个“名称”后跟一个“:”(冒号)
- “‘名称/值’ 对”之间使用“,”(逗号)分隔。
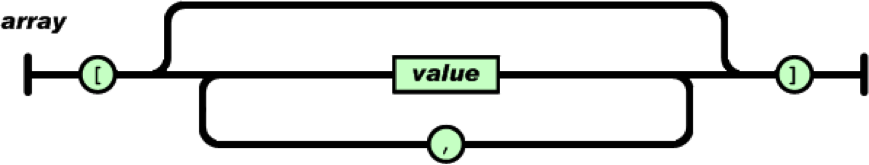
数组
数组是值(value)的有序集合。一个数组以“[”(左中括号)开始,“]”(右中括号)结束;值之间使用“,”(逗号)分隔。
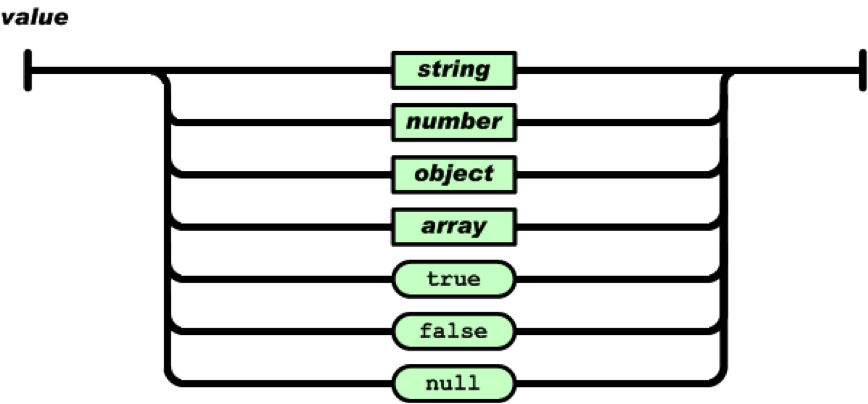
值
值(value)可以是双引号括起来的字符串(string)、数值(number)、true、false、 null、对象(object)或者数组(array)。因此可以递归嵌套。
json spirit部分源码分析
value的结构
enum Value_type{ obj_type, array_type, str_type, bool_type, int_type, real_type, null_type };
// 这个Value_type只是标识哪种类型
// Config 配置决定使用wstring或string以及map或者vector来实现
template< class Config >
class Value_impl
{
public:
typedef Config Config_type;
typedef typename Config::String_type String_type;// 这些typedef只是转发了Config的类型
typedef typename Config::Object_type Object;
typedef typename Config::Array_type Array;
typedef typename String_type::const_pointer Const_str_ptr; // eg const char*
Value_impl(); // creates null value
// 构造函数支持接受的类型,因为内部使用了boost::variant
Value_impl( Const_str_ptr value );
Value_impl( const String_type& value );
Value_impl( const Object& value );
Value_impl( const Array& value );
Value_impl( bool value );
Value_impl( int value );
Value_impl( boost::int64_t value );
Value_impl( boost::uint64_t value );
Value_impl( double value );
Value_impl( const Value_impl& other ); // 支持复制构造
bool operator==( const Value_impl& lhs ) const;
Value_impl& operator=( const Value_impl& lhs ); // 支持赋值
Value_type type() const;
bool is_uint64() const;
bool is_null() const;
// 获取当前值,当然你是知道要获取的类型的,类型不匹配时抛出异常(基于variant的实现)
const String_type& get_str() const;
const Object& get_obj() const;
const Array& get_array() const;
bool get_bool() const;
int get_int() const;
boost::int64_t get_int64() const;
boost::uint64_t get_uint64() const;
double get_real() const;
Object& get_obj(); // 注意返回非常量引用可以直接修改原内容
Array& get_array();
// get_value提供一个统一的接口,取得你想要的类型的值 Type val = val_impl. get_value< Type >();
template< typename T > T get_value() const;
static const Value_impl null;
private:
// 这个Variant是基于递归包装辅助类recursive_wrapper来实现的
// 从语法可以看到Variant可以是普通的值,也可以是数组或者对象,而数组或对象是可以基于value来组成的,从而导致循环依赖。
typedef boost::variant< String_type,
boost::recursive_wrapper< Object >, boost::recursive_wrapper< Array >,
bool, boost::int64_t, double > Variant;
// 三个数据成员
Value_type type_; // 表示类型
Variant v_; // 这个variaant对象存储着当前对象的类型信息和值。
bool is_uint64_;
};
配置Config的说明
对于vector的配置实现不作介绍。它的计算寻址写入以及之后对象内容的查询使用都是线性时间复杂度的;而基于map实现对象(object)是对数时间的。
template< class String > // String配置支持wstring 或者 string
struct Config_map
{
typedef String String_type;
// 配置真正的value类型,基于Value_impl实现
typedef Value_impl< Config_map > Value_type;
//数组是vector< Value_type >
typedef std::vector< Value_type > Array_type;
// 对象的类型 map
typedef std::map< String_type, Value_type > Object_type;
typedef typename Object_type::value_type Pair_type;
// 以下的三个静态函数只是用于语义动作时绑定使用的。对我们没有使用价值
// 如果基于Qi实现,直接使用phoenix来做语义动作,而无需到处分散的函数。
static Value_type& add( Object_type& obj,
const String_type& name, const Value_type& value )
{
return obj[ name ] = value;
}
static String_type get_name( const Pair_type& pair )
{
return pair.first;
}
static Value_type get_value( const Pair_type& pair )
{
return pair.second;
}
};
语法的大致情况
在 json_spirit_reader.cpp 中实现语法解析,大致介绍下结构。
(1)、Semantic_actions类来专门封装一个语义动作类。以下是它的成员:
Value_type& value_; // 对象或数组
Value_type* current_p_; // 当前被创建的对象或数组
vector< Value_type* > stack_; // 维持的一个船舰对象或数组的栈
String_type name_; // of current name/value pair
(2)、核心的语法定义
template< typename ScannerT >
class definition
{
public:
definition( const Json_grammer& self )
{
//...
// actual grammer
json_
= value_ | eps_p[ &throw_not_value ]
;
value_ // value 的定义,可以嵌套为object
= string_[ new_str ]
| number_
| object_
| array_
| str_p( "true" ) [ new_true ]
| str_p( "false" )[ new_false ]
| str_p( "null" ) [ new_null ]
;
object_
= ch_p('{')[ begin_obj ]
>> !members_
>> ( ch_p('}')[ end_obj ] | eps_p[ &throw_not_object ] )
;
members_
= pair_ >> *( ',' >> pair_ )
;
pair_ // 要放入map的pair: name/value 对
= string_[ new_name ]
>> ( ':' | eps_p[ &throw_not_colon ] )
>> ( value_ | eps_p[ &throw_not_value ] )
;
array_
= ch_p('[')[ begin_array ]
>> !elements_
>> ( ch_p(']')[ end_array ] | eps_p[ &throw_not_array ] )
;
elements_
= value_ >> *( ',' >> value_ )
;
string_
= lexeme_d // this causes white space inside a string to be retained
[
confix_p
(
'"',
*lex_escape_ch_p,
'"'
)
]
;
number_
= strict_real_p[ new_real ]
| int64_p [ new_int ]
| uint64_p [ new_uint64 ]
;
}
rule< ScannerT > json_, object_, members_, pair_, array_, elements_, value_, string_, number_;
const rule< ScannerT >& start() const { return json_; } //语法起点
};
理解json spirit的使用及注意事项
解析json字符串
首先,json解析得到的结构为对象(object)和数组(array),已经帮我们自定义了一些需要使用的类型:
例如:基于map和wstring的类型:
typedef Config_map< std::wstring > wmConfig;
typedef wmConfig::Value_type wmValue;
typedef wmConfig::Object_type wmObject;
typedef wmConfig::Array_type wmArray;
即 wmValue, wmObject 和 wmArray可以直接拿来使用的。
再把定义拿过来看清楚:
// 配置真正的value类型,基于Value_impl实现
typedef Value_impl< Config_map > Value_type;
//数组是vector< Value_type >
typedef std::vector< Value_type > Array_type;
// 对象的类型 map
typedef std::map< String_type, Value_type > Object_type;
- wmValue是
Value_impl< Config_map< std::wstring > >,从wmValue对象可以get得到真正包含在variant中的对象。它本身是variant对象。 - wmObject是
map< wstring, wmValue >与传统的map不一样,由于值是variant型,可以为指定的任意类型 - wmArray是
vector< wmValue >,也与普通vector的“单类型”不一样。
另一方面注意的就是,比如 m[“name”],vect[index]得到的是 wmValue类型,要得到真正类型,还需要调用get。而wmValue类型即Value_impl<Config>支持大量的构造函数,赋值函数,以及取值函数。(其实是variant的转发),使用非常方便。当然,我们知道想要得到的东西是对象还是数组,解析得到的类型也清楚,因为这是我们解析json码的初衷,如果类型不匹配抛出异常(实际由variant的get函数抛出)。
最终解析json,是很多全局的API(请查阅文档),比如:
bool read( const std::wstring& s, wmValue& value );// 从字符串取得json数据
bool read( std::wistream& is, wmValue& value );//从(文件)流去的数据
得到一个value,通过get_value得到对应的值(当然还可能是map, vector)。对于嵌套的map的值类型以及vector的值都是wmValue,可以get_value逐渐的继续深入解析。使用很清晰,意义很简单。
生成json字符串
这里仅说明一下:
void write( const wmValue& value, std::wostream& os );
void write_formatted( const wmValue& value, std::wostream& os );
std::wstring write( const wmValue& value );
std::wstring write_formatted( const wmValue& value );
通过提供wmValue 类型的value,一般为wmObject或者wmArray就可以得到一个value对应的json字符串。
