The network stack is a mostly single-threaded cross-platform library primarily for resource fetching. Its main interfaces are URLRequest and URLRequestContext.
- URLRequest, as indicated by its name, represents the request for a URL.
- URLRequestContext contains all the associated context necessary to fulfill the URL request, such as cookies, host resolver, proxy resolver, cache, etc.
- Many URLRequest objects may share the same URLRequestContext.
- Most net objects are not threadsafe, although the disk cache can use a dedicated thread, and several components (host resolution, certificate verification, etc.) may use unjoined worker threads.
- Since it primarily runs on a single network thread, no operation on the network thread is allowed to block. Therefore we use non-blocking operations with asynchronous callbacks (typically CompletionCallback).
Net Code Layout
- base - Grab bag of net utilities, such as host resolution, cookies, network change detection, SSL.
- disk_cache - Cache for web resources.
- ftp - FTP implementation. Code is primarily based on the old HTTP implementation.
- http - HTTP implementation.
- ocsp - OCSP implementation when not using the system libraries or if the system does not provide an OCSP implementation. Currently only contains an NSS based implementation.
- proxy - Proxy (SOCKS and HTTP) configuration, resolution, script fetching, etc.
- socket - Cross-platform implementations of TCP sockets, “SSL sockets”, and socket pools.
- socket_stream - socket streams for WebSockets
- spdy - SPDY implementation.
- url_request - URLRequest, URLRequestContext, and URLRequestJob implementations.
- websockets - WebSockets implementation.
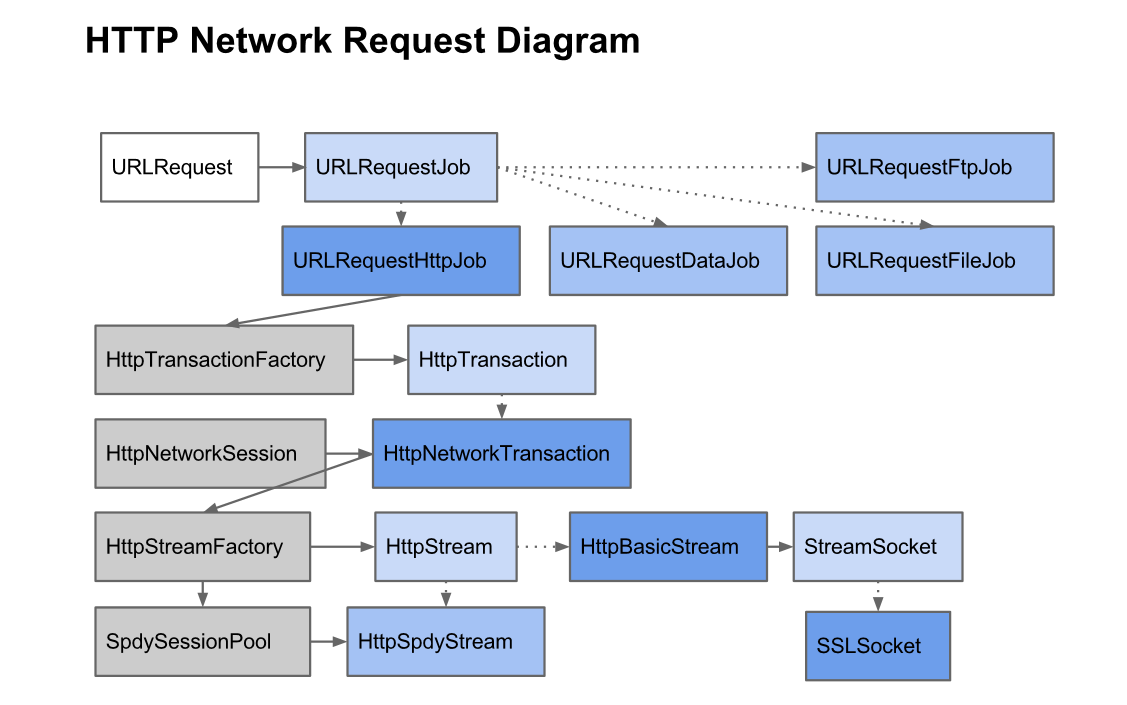
HTTP Network Diagram
URLRequest
class URLRequest {
public:
// Construct a URLRequest for |url|, notifying events to |delegate|.
URLRequest(const GURL& url, Delegate* delegate);
// Specify the shared state
void set_context(URLRequestContext* context);
// Start the request. Notifications will be sent to |delegate|.
void Start();
// Read data from the request.
bool Read(IOBuffer* buf, int max_bytes, int* bytes_read);
};
class URLRequest::Delegate {
public:
// Called after the response has started coming in or an error occurred.
virtual void OnResponseStarted(...) = 0;
// Called when Read() calls complete.
virtual void OnReadCompleted(...) = 0;
};
- When a URLRequest is started, the first thing it does is decide what type of URLRequestJob to create.
- The main job type is the
URLRequestHttpJobwhich is used to fulfillhttp://requests. - There are a variety of other jobs, such as
URLRequestFileJob (file://),URLRequestFtpJob (ftp://),URLRequestDataJob (data://), and so on. - If you customize chromium for your embed app, then you can customize protocols ( such as
myscheme://xxx) or customize jobs.
URLRequestHttpJob
URLRequestHttpJob is used for dealing with http request, resource may be cached or to download from remote web service.
- URLRequestHttpJob will first identify the cookies to set for the HTTP request, which requires querying the CookieMonster in the request context. This can be asynchronous since the CookieMonster may be backed by an sqlite database.
- After doing so, it will ask the request context’s HttpTransactionFactory to create a HttpTransaction. Typically, the HttpCache will be specified as the HttpTransactionFactory. The HttpCache will create a HttpCache::Transaction to handle the HTTP request.
- The HttpCache::Transaction will first check the HttpCache (which checks the disk cache) to see if the cache entry already exists. If so, that means that the response was already cached, or a network transaction already exists for this cache entry, so just read from that entry.
- If the cache entry does not exist, then we create it and ask the HttpCache’s HttpNetworkLayer to create a HttpNetworkTransaction to service the request.
- The HttpNetworkTransaction is given a HttpNetworkSession which contains the contextual state for performing HTTP requests. Some of this state comes from the URLRequestContext.
Example
The example shows to use net::URLFetcher to fetch data from a url.
class SyncUrlFetcher : public net::URLFetcherDelegate {
public:
SyncUrlFetcher(const GURL& url,
net::URLRequestContextGetter* getter,
std::string* response)
: url_(url), getter_(getter), response_(response), event_(false, false) {}
virtual ~SyncUrlFetcher() {}
bool Fetch() {
getter_->GetNetworkTaskRunner()->PostTask(
FROM_HERE,
base::Bind(&SyncUrlFetcher::FetchOnIOThread, base::Unretained(this)));
// sync fetch, wait for complete
event_.Wait();
return success_;
}
void FetchOnIOThread() {
fetcher_.reset(net::URLFetcher::Create(url_, net::URLFetcher::GET, this));
fetcher_->SetRequestContext(getter_);
fetcher_->Start();
}
virtual void OnURLFetchComplete(const net::URLFetcher* source) OVERRIDE {
success_ = (source->GetResponseCode() == 200);
if (success_)
success_ = source->GetResponseAsString(response_);
fetcher_.reset(); // Destroy the fetcher on IO thread.
// complete and signal
event_.Signal();
}
private:
GURL url_;
net::URLRequestContextGetter* getter_;
std::string* response_;
base::WaitableEvent event_;
scoped_ptr<net::URLFetcher> fetcher_;
bool success_;
};
// Fetch data from url sync, MUST NOT call on chrome IO thread
// can be used on custom worker thread
inline bool FetchUrl(const std::string& url,
net::URLRequestContextGetter* getter,
std::string* response) {
return SyncUrlFetcher(GURL(url), getter, response).Fetch();
}
reference
http://www.chromium.org/developers/design-documents/network-stack https://insouciant.org/tech/connection-management-in-chromium/
