mpl致力于操作编译期的静态语言设施,元数据和类型都具有不变性,与纯函数式编程有相似之处。
mpl提供了模板元编程需要的基础框架:
- 序列,
- 迭代器,
- 算法,
- 还有一些如fold之类的基础元函数。
序列
编译期类型序列是C++模板元编程中的一个基本概念。MPL 将类型序列的重要性视为很多高级元编程设计的基础构件,提供了一套正式的基本框架。
为了简单起见,先写一个相对通用的打印类型序列方法:
// print_seq.h
#ifndef PRINT_SEQ_H
#define PRINT_SEQ_H
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\mpl\deref.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\begin_end.hpp>
namespace print_seq
{
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
namespace detail
{
template<typename T>
struct member_helper
{
typedef void type;
};
//判断是否有内嵌的value_type类型
template<typename T, typename U = void> //用默认模板参数指示默认情况
struct has_value_member
{
static const bool value = false;
};
template<typename T>//偏特化,优先去适配从T萃取类型, T有内置的type时选择
struct has_value_member<T, typename member_helper<typename T::value_type>::type >
{
static const bool value = true;
};
template<typename T, bool hasValue>
struct PrintType
{
static void print()
{
std::cout << typeid( T ).name() << std::endl;
}
};
template<typename T>
struct PrintType<T, true>
{
static void print() { std::cout << T::value << std::endl; }
};
template<typename Beg, typename End >
struct PrintSequenceHelper
{
static void print()
{
typedef typename mpl::deref<Beg>::type value_type;
PrintType< value_type, has_value_member< value_type >::value >::print();
PrintSequenceHelper<mpl::next<Beg>::type, End>::print();
}
};
template<typename Iter>
struct PrintSequenceHelper<Iter, Iter>
{
static void print() {}
};
}
// print
template<typename Beg, typename End>
void PrintSequence()
{
detail::PrintSequenceHelper<Beg, End>::print();
}
template<typename S>
void PrintSequence()
{
detail::PrintSequenceHelper<mpl::begin<S>::type, mpl::end<S>::type>::print();
}
}// print_seq
#endif // PRINT_SEQ_H
类
- 1、vector
vector 是一个 不定长, 随机访问, 可扩展 的类型序列,它支持在两端的常量时间的元素插入和删除操作,以及在中间的线性时间的元素插入和删除操作。
定义类型序列:
vector<t1,t2,... tn> vectorn<t1,t2,... tn> vector<t1,t2,... tn>::type 以上三种写法等价迭代器
begin<v>::type :指向 v 的开头的迭代器 end<v>::type :指向 v 的结尾的迭代器序列大小属性
size<v>::type :v的大小 empty<v>::type :返回布尔整型常量C满足:C::value == true 当且仅当v为空读取元素
front<v>::type :首个元素类型 back<v>::type :最后一个元素类型 at<v,n>::type :支持随机访问,第n::value个元素类型序列扩展操作
insert<v,pos,x>::type :在某个迭代器位置插入一个元素 新的 vector,具有以下元素:[begin<v>::type, pos), x, [pos, end<v>::type); insert_range<v,pos,r>::type :插入一个序列 新的 vector,具有以下元素:[begin<v>::type, pos), [begin<r>::type, end<r>::type) [pos, end<v>::type); erase<v,pos>::type :删除迭代器对于的元素 新的 vector,具有以下元素:[begin<v>::type, pos), [next<pos>::type, end<v>::type); erase<v,pos,last>::type :删除迭代器对[ pos, last )指定的区间 新的 vector,具有以下元素:[begin<v>::type, pos), [last, end<v>::type); clear<v>::type :清空 空的 vector push_back<v,x>::type 新的 vector,具有以下元素:[begin<v>::type, end<v>::type), x pop_back<v>::type 新的 vector,具有以下元素:[begin<v>::type, prior< end<v>::type >::type); push_front<v,x>::type 新的 vector,具有以下元素:x, [begin<v>::type, end<v>::type) pop_front<v>::type 新的 vector,具有以下元素:[next< begin<v>::type >::type, end<v>::type)
例如:
#include "print_seq.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <boost\mpl\vector.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\push_back.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\insert.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
int main()
{
typedef mpl::vector<int, std::string> my_vector;
typedef mpl::push_back< my_vector, double >::type pb_vector;
print_seq::PrintSequence<pb_vector>();
std::cout << "\n";
typedef mpl::next< mpl::begin<pb_vector>::type >::type pos_iter;
typedef mpl::insert< pb_vector, pos_iter, std::vector<int> >::type new_vector;
print_seq::PrintSequence<new_vector>();
return 0;
}
输出:
int
class std::basic_string<char,struct std::char_traits<char>,class std::allocator<char> >
double
int
class std::vector<int,class std::allocator<int> >
class std::basic_string<char,struct std::char_traits<char>,class std::allocator<char> >
double
- 2、list
list 是一个 不定长, 前向, 可扩展 的类型序列,它支持在序列头部的常量时间的元素插入和删除操作,以及在序列中部及尾部的线性时间的元素插入和删除操作。
定义序列
list<t1,t2,... tn> listn<t1,t2,... tn> list<t1,t2,... tn>::type listn<t1,t2,... tn>::type迭代器
begin<l>::type :通过迭代器可以遍历list end<l>::type序列大小属性
size<l>::type empty<l>::type读取元素
front<l>::type :list只有front元素可以读取序列扩展操作
insert<l,pos,x>::type insert_range<l,pos,r>::type erase<l,pos>::type erase<l,pos,last>::type clear<l>::type push_front<l,x>::type pop_front<l>::type- 3、deque
与vector的行为基本一致
- 4、set
set 是一个 不定长, 关联, 可扩展 的类型序列,它支持常量时间的元素插入、删除和成员检查。set 中的每个键最多有一个元素。
- 关于关联序列:
关联序列 是一种 前向序列,它可以基于键值高效地取出元素。与C++标准库中的关联容器不同,MPL关联序列没有关联的排序关系。取而代之的是,使用类型标识来实现键值上的等价关系,且在迭代中对序列元素的遍因历顺序是未指定的。
定义类型
set<t1,t2,... tn> setn<t1,t2,... tn> set<t1,t2,... tn>::type setn<t1,t2,... tn>::type迭代器
begin<s>::type end<s>::type容器大小
size<s>::type empty<s>::type首个序列元素
front<s>::type元素检查
has_key<s,k>::type :容器s中含有k,则返回C::value == true count<s,k>::type :s 中键为 k 的数量,等价于count_if< s,is_same<_,T> >::type order<s,k>::type :如果 has_key<s,key>::value == true, 则为一个唯一的无符号 整型常量,与 s 中的 key 相关联; 否则,等价于 void_.返回与k关联的元素
at<s,k>::type :如果存在k,则为k类型;否则为mpl::void_类型 at<s,k,def>::type :支持默认类型 key_type<s,x>::type :与x等价 value_type<s,x>::type :与x等价序列扩展操作
insert<s,x>::type insert<s,pos,x>::type erase_key<s,k>::type erase<s,pos>::type clear<s>::type
例如:
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\mpl\set.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\assert.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\size.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\empty.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\at.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
int main()
{
typedef mpl::set<int,long,double, mpl::int_<5> > s;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_RELATION( mpl::size<s>::value, ==, 4 );
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_NOT(( mpl::empty<s> ));
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( boost::is_same< mpl::at<s,int>::type, int > ));
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( boost::is_same< mpl::at<s,long>::type, long > ));
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( boost::is_same< mpl::at<s, mpl::int_<5> >::type, mpl::int_<5> > ));
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( boost::is_same< mpl::at<s,char>::type, mpl::void_ > ));
return 0;
}
- 5、map
map 是一个 不定长, 关联, 可扩展 的类型对的序列,它支持常量时间的元素插入和删除以及成员检查。map 中的每个键值最多包含一个元素。
定义序列
map<p1,p2,... pn> :其中p为pair< Key, Value > mapn<p1,p2,... pn> map<p1,p2,... pn>::type mapn<p1,p2,... pn>::type迭代器
begin<m>::type end<m>::type容器大小
size<m>::type empty<m>::type首个序列元素
front<m>::type元素检查
has_key<m,k>::type :容器s中含有k,则返回C::value == true count<m,k>::type :s 中键为 k 的数量,等价于count_if< s,is_same<_,T> >::type order<m,k>::type :如果 has_key<s,key>::value == true, 则为一个唯一的无符号 整型常量,与 s 中的 key 相关联; 否则,等价于 void_.返回与k关联的元素
at<m,k>::type :如果存在k,则为与k对应的值类型;否则为mpl::void_类型 at<m,k,def>::type :支持默认类型 key_type<m,x>::type :等同于 x::first value_type<m,x>::type :等同于 x::second序列扩展操作
insert<m,x>::type 新的map序列m,并且满足:at< t, key_type<m,x>::type >::type等同于 value_type<m,x>::type. insert<m,pos,x>::type erase_key<m,k>::type erase<m,pos>::type clear<m>::type
例如:
typedef map
<
pair<int,unsigned>
, pair<char,unsigned char>
, pair<long_<5>,char[17]>
, pair<int[42],bool>
> m;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_RELATION( size<m>::value, ==, 4 );
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_NOT(( empty<m> ));
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( is_same< at<m,int>::type, unsigned > ));
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( is_same< at<m,long_<5> >::type, char[17] > ));
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( is_same< at<m,int[42]>::type, bool > ));
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( is_same< at<m,long>::type, void_ > ));
- 6、range_c
- range_c 是一个有序的 整型常量 随机访问序列。注意,由于它不是 可扩展序列,类似于 push_front 这样的序列构造元函数以及类似于 replace 这样的转变算法不能直接应用。
说明:
range_c<T,n,m>
range_c<T,n,m>::type
T 是任意的整型类型,而 n 和 m 为类型 T 的整型常量值,定义一个有序的整型常量包装器的 随机访问序列,对应于半开区间 [n, m):
integral_c<T,n>, integral_c<T,n+1>,... integral_c<T,m-1>.
begin<r>::type
end<r>::type
size<r>::type
empty<r>::type
front<r>::type
back<r>::type
at<r,n>::type
例如:
typedef range_c<int,0,10> range10;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_RELATION( size<range10>::value, ==, 10 );
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_RELATION( back<range10>::type::value, ==, 9 );
- 7、vector_c
- vector_c 是 整型序列包装器 的一个 vector。具有vector的所有操作属性,仅元素内容不同,都是整型常量。
定义序列:
vector_c<T,c1,c2,... cn>
vectorn_c<T,c1,c2,... cn>
vector_c<T,c1,c2,... cn>::type
vectorn_c<T,c1,c2,... cn>::type
一个 vector,其元素为整型常量包装器 integral_c<T,c1>, integral_c<T,c2>, ... integral_c<T,cn>;
其中,integral_c<t,c>是一个整型常量 x 满足 x::value == c 和 x::value_type 为 t.
- 8、list_c
- list_c 是 整型序列包装器 的一个 list。它具有 list 的所有特性和要求。
- 9、set_c
- set_c 是 整型序列包装器 的一个 set。它具有 set 的所有特性和要求。
- 10、string
- string 是一个
不定长, 双向的, 可扩展的字符整型序列包装器,支持在两端的分摊常量时间的元素插入和删除,以及在中间的线性时间的元素插入和删除。给 string 的参数是多字符字面值,可以是任何可读语法的编译期字符串。string 也可以作为 c_str 元函数的参数,生成一个以null-结尾的字符数组,与运行时字符串操作函数进行互动。
基本操作与vector一致,但是多了个c_str元函数。
定义序列
string<c1,c2,... cn> :c可以为任意多个字符 string<c1,c2,... cn>::type迭代器
begin<s>::type end<s>::type size<s>::type empty<s>::type front<s>::type back<s>::type扩展操作
insert<s,pos,x>::type insert_range<s,pos,r>::type erase<s,pos>::type erase<s,pos,last>::type clear<s>::type push_back<s,x>::type pop_back<s>::type push_front<s,x>::type pop_front<s>::type字符串支持
c_str<s>::value 一个以null-结尾的字节串,满足 : c_str<s>::value[n] 等于 s 中第 n-个字符,且 c_str<s>::value[size<s>::type::value] 为 '\0'。
例如:
typedef mpl::string<"hell","o wo","rld"> hello;
typedef mpl::push_back<hello, mpl::char_<'!'> >::type hello2;
BOOST_ASSERT(0 == std::strcmp(mpl::c_str<hello2>::value, "hello world!"));
视图
视图 是一个序列适配器, 它根据一个或多个底层的序列生成改变了的表示。 视图是惰性的,即它只在需要时才计算其中的元素。类似于 short-circuit 逻辑操作 和 eval_if,视图可以避免过早求值的错误和节省不必要的计算开销。
通过使用视图,许多算法可以以更为简单、更为精确、更有表现力的方法来实现。
1、empty_sequence
struct empty_sequence;
表示不包含元素的序列。
typedef begin<empty_sequence>::type first;
typedef end<empty_sequence>::type last;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( is_same<first,last> ));
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_RELATION( size<empty_sequence>::value, ==, 0 );
2、filter_view
template
<
typename Sequence
, typename Pred
>
struct filter_view;
一个视图,由 Sequence 中满足谓词 Pred 的元素组成。
例如:找出序列中最大的浮点类型
typedef vector<int,float,long,float,char[50],long double,char> types;
typedef max_element<
transform_view< filter_view< types,boost::is_float<_> >, size_of<_> >
>::type iter;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( is_same< deref<iter::base>::type, long double > ));
3、iterator_range
template
<
typename First
, typename Last
>
struct iterator_range;
一个视图,由一对迭代器指定的序列子集中的元素组成。
4、joint_view
template
<
typename Sequence1,
typename Sequence2
>
struct joint_view;
一个视图,由 Sequence1 和 Sequence2 的元素连接而成。
5、single_view
template
<
typename T
>
struct single_view;
一个视图,含任意类型 T 的单元素序列。
6、transform_view
template
<
typename Sequence
, typename F
>
struct transform_view;
一个视图,由 Sequence 的所有元素转化而成的序列。
7、zip_view
template
<
typename Sequences // 由序列组成的序列
>
struct zip_view;
提供多个序列的 “压缩” 视图;即将多个序列表示为一个序列,其中每个元素为由各个 Sequences 的对应元素组成的序列。
关于zip_view的长度:
v 是一个 zip_view 实例,seqs 是一个由 n 个 前向序列 组成的 前向序列:
size<v>::type 等价于
deref< min_element< transform_view< seqs, size<_1> > >::type >::type::value;
例子:
typedef vector_c<int,1,2,3,4,5> v1;
typedef vector_c<int,5,4,3,2,1> v2;
typedef vector_c<int,1,1,1,1,1> v3;
typedef transform_view
<
zip_view< vector<v1,v2,v3> >
, unpack_args< plus<_1,_2,_3> > // 将接受3个参数转为接受序列
> sum;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( equal< sum, vector_c<int,7,7,7,7,7> > ));
固有元函数
at
template < typename Sequence , typename N > struct at; template < typename AssocSeq , typename Key , typename Default = unspecified > struct at;
at 是一个重载的名字:
at<Sequence,N>返回 前向序列 Sequence 中从开头计第 N 个元素。at<AssocSeq,Key,Default>返回 关联序列 AssocSeq 中与 Key 关联的第一个元素,如果没有这样的元素则返回 Default.at_c
template < typename Sequence , long n > struct at_c;
返回一个与序列中第 n 个元素相同的类型。at_c<Sequence,n>::type 是 at< Sequence, long_<n> >::type 的缩写。
back
template< typename Sequence > struct back;
返回序列中最后一个元素。
front
template< typename Sequence > struct front;
返回序列中的第一个元素。
begin
template< typename X > struct begin;
返回一个迭代器,指向序列的第一个元素。如果其参数不是一个 前向序列, 则返回 void_.
end
template< typename X > struct end;
返回序列的 past-the-end 迭代器。如果其参数不是一个 前向序列, 返回 void_.
empty
template< typename Sequence > struct empty;
返回一个 整型常量 c 满足 c::value == true 当且仅当序列为空。
size
template< typename Sequence > struct size;
size 返回序列中的元素数量,即区间 [begin<Sequence>::type, end<Sequence>::type) 中的元素数量。
clear
template< typename Sequence > struct clear;
返回一个与 Sequence 概念相同的 空序列。
erase
template < typename Sequence , typename First , typename Last = unspecified > struct erase;
erase 从序列中的任意位置开始删除一个或多个连续元素。删除多个元素时,要指定Last迭代器。
insert
template < typename Sequence , typename Pos , typename T > struct insert; template < typename Sequence , typename T > struct insert;
insert 是一个 重载的名字:
insert<Sequence,Pos,T>将类型 T 插入于 Sequence 中的任意位置 Pos. 如果Sequence 是 可扩展关联序列 的 model,则Pos 被忽略。insert<Sequence,T>是insert<Sequence,Pos,T>的缩写,当Sequence 是 可扩展关联序列 的 model 时。序列首尾操作
pop_back pop_front push_back push_fronterase_key
template < typename AssocSeq , typename Key > struct erase_key;
删除 可扩展关联序列 AssocSeq 中与键 Key 相关联的元素。
- has_key
如果 Sequence 包含键值为 Key 的元素,则返回一个真值的 整型常量.
insert_range
template < typename Sequence , typename Pos , typename Range // 待插入的序列 > struct insert_range;
insert_range 将某个区间的元素插入到序列的任意位置。
is_sequence
template< typename X > struct is_sequence;
返回一个布尔 整型常量 c,c::value == true 当且仅当 X 是 前向序列 的 model.
order
template < typename Sequence , typename Key > struct order;
返回一个唯一的无符号 整型常量,它与 Sequence 中的键值 Key 相关联。如果不存在Key,则返回void_。
- sequence_tag
sequence_tag 是一个 tag 元函数,用于所有 tag 分派 固有序列操作。
value_type
template < typename Sequence , typename X > struct value_type;
返回用于在 Sequence 中标识 X 的 值。
typedef value_type< map<>,pair<int,unsigned> >::type v;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( is_same< v, unsigned > ));
key_type
template < typename Sequence , typename X > struct key_type;
返回用于在 Sequence 中标识 X 的 键。
typedef key_type< map<>,pair<int,unsigned> >::type k;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( is_same< k,int > ));
迭代器
1、advance
template
<
typename Iterator
, typename N
>
struct advance;
将 Iterator 移动 N 个位置。对于 双向 和 随机访问 迭代器,距离可以为负。
2、distance
template
<
typename First
, typename Last
>
struct distance;
返回前向迭代器 First 和 Last 迭代器间的距离,即一个 整型常量 n 满足 advance<First,n>::type 等同于 Last.
3、next
template
<
typename Iterator
>
struct next;
返回序列中的下一个迭代器。
注意: next 有多个重载的含义,取决于其参数的类型。例如,如果 X 是一个 整型常量,next<X> 返回相同类型的一个递增 整型常量。
4、prior
template
<
typename Iterator
>
struct prior;
返回双向序列中的前一个迭代器。
注意: prior 有多个重载的含义,取决于其参数的类型。例如,如果 X 是一个 整型常量,prior<X> 返回相同类型的一个递减后的 整型常量。
5、deref
template
<
typename Iterator
>
struct deref;
提取迭代器所指向的元素。
6、iterator_category
template
<
typename Iterator
>
struct iterator_category;
返回以下迭代器类别 tag 之一:
- forward_iterator_tag
- bidirectional_iterator_tag
- random_access_iterator_tag
元函数
MPL 包含了大量预定义的元函数,它们可以大致分为两类:
- 通用元函数, 处理有条件 类型选择 以及高阶元函数 调用, 合成, 以及 参数绑定
- 数值元函数, 封装内建和用户定义的 算术, 比较, 逻辑, 和 位操作 操作。
定义
元函数 是一个类或类模板,表示一个可以在编译期被调用的函数。调用一个带参数的元函数的方法是,以特定的模板参数(元函数参数)实例化该类模板;元函数的结果可通过实例的内嵌 type typedef 来访问。所有元函数的参数都必须是类型(即只允许使用 类型模板参数)。一个元函数的参数数量是可变的。无参元函数 可表示为一个带有内嵌 type typename 成员的(模板)类。
- 元函数类 元函数的一种特定表示方式,以支持高阶元编程。具体地说,它是一个带有名为 apply 的公有访问的内嵌 元函数 的类。对应地,元函数类的调用被定义为对内嵌的 apply 元函数的调用。
- Lambda Expression 是一个编译期可调用的实体,具有以下两种形式之一:元函数类、占位符表达式。
- 占位符表达式 是一个类型,它要么是一个 占位符,要么是至少有一个参数为 占位符表达式 的特化类模板。
如果 X 是一个类模板,而 a1,... an 为任意类型,则 X<a1,...,an> 为 占位符表达式,当且仅当以下所有条件被满足:
- 至少有一个模板参数
a1,... an为 占位符 或 占位符表达式。 - X 的所有模板参数,包括缺省的参数,都是类型。
- X 的模板参数数量,包括缺省的参数,小于或等于 BOOST_MPL_LIMIT_METAFUNCTION_ARITY 配置宏 的值。
- Tag分派元函数
- 是一种 元函数,在其实现中采用了tag分派技术来构建一个基础架构以便于覆盖或扩展元函数的行为。
- 数值元函数
- 是一种 Tag 分派元函数,它提供内建的基础架构以便于实现混合类型操作。
- 平凡元函数
- 以类类型 x 为单个参数,返回 x 的内嵌类型成员 x::name, 其中 name 为表示由特定元函数实例访问的实际成员名的占位符号。作为惯例,MPL中的所有 平凡元函数 以它们提供访问的成员名为名字。例如,名为 first 的 平凡元函数 访问 x 的内嵌成员 ::first.
类型选择元函数
if_ :if_< C, T1, T2 >::type 其中C为整型常量,等价于if_c< C::value, T1, T2 >
if_c :if_c< c, T1, T2 >::type,其中c为bool类型
eval_if :eval_f<C, F1, F2>::type,当C::value为true时,则选择F1::type,否则F2::type
eval_if_c
说明:
带eval版本,最后的结果是多计算了下模板参数类型F内嵌的type,而不是它本身,这样的好处的缓式计算,只计算需要计算的F::type。
例如:
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\type_traits.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\if.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\identity.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
int main()
{
typedef mpl::if_< boost::is_same<int,double>, int, double >::type if_type1;
typedef mpl::eval_if_c< boost::is_same<int,double>::value, mpl::identity<int>, mpl::identity<double> >::type if_type2;
std::cout << typeid(if_type1).name() << "\n";
std::cout << typeid(if_type2).name() << "\n";
return 0;
}
调用apply
1、apply
template
<
typename F
, typename A1 = unspecified
// ...
, typename An = unspecified
>
struct apply;
以参数 A1,… An 调用 元函数类 或 Lambda 表达式 F。
typedef apply<f,a1,...an>::type t; 等价于
typedef apply_wrap< lambda<f>::type,a1,... an>::type t;.
例如:
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\mpl\apply.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\int.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\lambda.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
template< typename N1, typename N2 >
struct int_plus
: mpl::int_<( N1::value + N2::value )>
{
};
struct int_plus_apply
{
template< typename N1, typename N2 >
struct apply
{
typedef mpl::int_< N1::value + N2::value > type;
};
};
int main()
{
// apply应用于 lambda表达式
typedef mpl::apply< int_plus<mpl::_1,mpl::_2>, mpl::int_<2>, mpl::int_<3> >::type r1;
// apply应用于元函数类
typedef mpl::apply< int_plus_apply, mpl::int_<2>, mpl::int_<3> >::type r2;
std::cout << r1::value << " " << r2::value << "\n";
return 0;
}
2、apply_wrap
template< typename F, typename A1,... typename An >
struct apply_wrapn;
apply_wrap 形式只是 F::apply<A1,... An>::type / F::apply::type 表达式的一个语法包装(因此而得名而已。因此不支持lambda表达式,只能用于元函数类。它们提供了更简明的表示法以及比底层结构更高的可移植性,而付出的代价则是一次额外的模板实例化。
注意:
apply用于对lambda表达式的调用,但是apply_wrapN除了可以调用之外,还可以继续封装成占位符表达式等。
例如:
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\mpl\apply.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\apply_wrap.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\int.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\lambda.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
struct int_plus_apply
{
template< typename N1, typename N2 >
struct apply
{
typedef mpl::int_< N1::value + N2::value > type;
};
};
int main()
{
// apply_wrap2继续封装
typedef mpl::apply_wrap2< int_plus_apply, mpl::int_<2>, mpl::_1 > plus2;
// apply只能调用
typedef mpl::apply< plus2, mpl::int_<3> >::type r2;
// apply_wrapN不带更多的占位符时,取type即为调用
typedef mpl::apply_wrap1< mpl::lambda<plus2>::type, mpl::int_<3> >::type r3;
std::cout << r2::value << " " << r3::value << "\n";
return 0;
}
输出:5 5
3、unpack_args
template< typename F >
struct unpack_args;
一个高阶的简单转化,将一个 n-元 Lambda 表达式 F 转化为一个单参元函数类 g,接受由原来的n个参数所组成的序列为单个参数。
例如:
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\mpl\unpack_args.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\int.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\lambda.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\vector.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
template< typename N1, typename N2 >
struct int_plus
: mpl::int_<( N1::value + N2::value )>
{
};
int main()
{
// 封装成接受序列的模板元函数类
typedef mpl::unpack_args< int_plus<mpl::_1, mpl::_2> > FunType;
std::cout << mpl::apply< FunType, mpl::vector< mpl::int_<2>, mpl::int_<3> > >::type::value << "\n";
return 0;
}
合成与参数绑定
1、占位符
占位符的形式为 _n,无数字的占位符 _ (下划线)在绑定和 lambda 表达式中具有 特殊的意义。
2、lambda
将占位符表达式转化为元函数类
template
<
typename X,
typename Tag = unspecified
>
struct lambda;
如果 X 是一个 占位符表达式,则将 X 转化为对应的 元函数类,否则返回 X.
例如:
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\mpl\apply.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\int.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\lambda.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
template< typename N1, typename N2 >
struct int_plus
: mpl::int_<( N1::value + N2::value )>
{
};
int main()
{
typedef mpl::lambda< int_plus<mpl::_1, mpl::int_<5>> >::type F;
std::cout << mpl::apply< F, mpl::int_<5> >::type::value << "\n";
std::cout << F::apply< mpl::int_<10> >::type::value << "\n";
return 0;
}
3、bind
template
<
typename F
, typename A1 = unspecified
// ...
, typename An = unspecified
>
struct bind;
bind 是一个高阶基本模板,用于 元函数类 合成和参数绑定,得到新的元函数类。本质上,它是 Boost.Bind 和 Boost.Lambda 库所提供的运行期功能在编译期中的对应物。
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\mpl\apply.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\int.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\lambda.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\bind.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
struct ArguFun
{
template<typename T, typename U>
struct apply
{
typedef U type;
};
};
int main()
{
typedef mpl::bind< ArguFun, mpl::_1, double > bind_f;
std::cout << typeid( bind_f::apply<int>::type ).name() << "\n";
std::cout << typeid( mpl::apply< bind_f, int >::type ).name() << "\n";
return 0;
}
4、quote
template
<
template< typename P1,... typename Pn > class F, // 模板的模板参数
typename Tag = unspecified
>
struct quoten;
quoten 是一个高阶基本模板,它包装一个 n-元 元函数 以创建一个相应的 元函数类。
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\type_traits.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\apply.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\int.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\lambda.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\quote.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
template<typename T>
struct AddPointer
{
typedef typename boost:: add_pointer<T>::type type;
};
template<typename T>
struct dummy
{
};
int main()
{
// 对于内嵌type的元函数,创建的元函数类apply时计算对应的type:int*
std::cout << typeid( mpl::quote1< AddPointer>::apply<int>::type ).name() << "\n";
// 没有内嵌type,则简单计算为原元函数的实例化:dummy<int>
std::cout << typeid( mpl::quote1< dummy >::apply<int>::type ).name() << "\n";
return 0;
}
5、arg
template< int n > struct arg;
template<> struct arg<1>
{
template< typename A1,... typename An = unspecified >
struct apply
{
typedef A1 type;
};
};
// ...
template<> struct arg<n>
{
template< typename A1,... typename An >
struct apply
{
typedef An type;
};
};
arg<n> 特化类是一个 元函数类,返回其参数中的第 n 个参数。
6、protect
template< typename F>
struct protect;
protect 是一个用于 元函数类 的身份包装器,防止其参数被识别为 绑定表达式( bind )。
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\type_traits.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\apply.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\lambda.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\quote.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\protect.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\assert.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
using namespace mpl;
struct f
{
template< typename T1, typename T2 >
struct apply
{
typedef T2 type;
};
};
int main()
{
typedef bind< quote3<if_>, _1, _2, bind<f,_1,_2> > b1;
typedef bind< quote3<if_>, _1, _2, protect< bind<f,_1,_2> > > b2;
typedef apply_wrap2< b1, false_, char >::type r1; // char
// protect< bind<f,_1,_2> >
typedef apply_wrap2< b2, false_, char >::type r2;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT( (boost::is_same< r1, char >) );
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT( (boost::is_same< r2, protect< bind<f,_1,_2> > >) );
return 0;
}
分析:
- 对于b1,首先是一个元函数类,
bind< quote3<if_>, _1, _2, bind<f, _1, _2> >注意到bind<f,_1,_2>直接作为模板参数,占位符直接暴露,对外部有效,这样apply_wrap2<b1, false_, char>::type,由于_1为false_,则选择bind<f, false_, char>,apply后得到char。 - 对于b2,内嵌的bind表达式被protect保护,外层的调用,不会替换内部的占位符。
算术操作(#include <boost/mpl/arithmetic.hpp> )
针对整型常量的计算:
- plus :连加
- minus :连减
- times :连乘
- divides :连除
- modulus :取模
- negate :取相反数
比较 (#include <boost/mpl/comparison.hpp> )
针对整型常量的比较:
- less
- less_equal
- greater
- greater_equal
- equal_to
- not_equal_to
逻辑操作 (#include <boost/mpl/logical.hpp> )
- and_
返回对其参数进行短路方式的 逻辑与
&&操作的结果。template < typename F1 , typename F2 ... , typename Fn = unspecified > struct and_;
即:对于任意无参元函数 f1, f2,… fn:
typedef and_<f1,f2,...,fn>::type r;
- r 为 false_ 如果
f1::type::value, f2::type::value,... fn::type::value表达式之一的求值结果等价于 false, 否则为 true_; - 确保求值从左到右进行;
- 在第一个求值结果为 false 的 fi 元函数之后的参数不会被求值。
- or_
- 返回对其参数进行短路方式的 逻辑或
||操作的结果。 - not_
返回对其参数进行 逻辑否
!操作的结果。template< typename F > struct not_; 要求F为无参元函数
位操作 (#include <boost/mpl/bitwise.hpp> )
针对整型常量进行位操作:
- bitand_
- bitor_
- bitxor_
- shift_left
- shift_right
平凡元函数
- first ::
first<X>::type等价于x::first - second
- base
字符串操作c_str (#include <boost/mpl/string.hpp> )
template< typename Sequence >
struct c_str;
c_str 将 整型常量 的 前向序列 Sequence 转换为一个包含相同序列的以null-结尾的字节串。
c_str<s>::value; 等价于
char const value[] = {
at<s, 0>::type::value
, ...
, at<s, size<s>::value-1>::type::value
, '\0'
};
其他元函数
- identity
identity<x>::type 为x自身
- always
always<X> 特化类是一个变长参数的元函数类,它总是返回类型 X, 不管传入的参数数量与类型。
实现:
template< typename Value >
struct always
{
template<
typename T
BOOST_MPL_PP_NESTED_DEF_PARAMS_TAIL(1, typename T, na)
>
struct apply
{
typedef Value type;
};
};
BOOST_MPL_AUX_ARITY_SPEC(1, always)
inherit
template < typename T1 , typename T2 ... , typename Tn = unspecified > struct inherit;
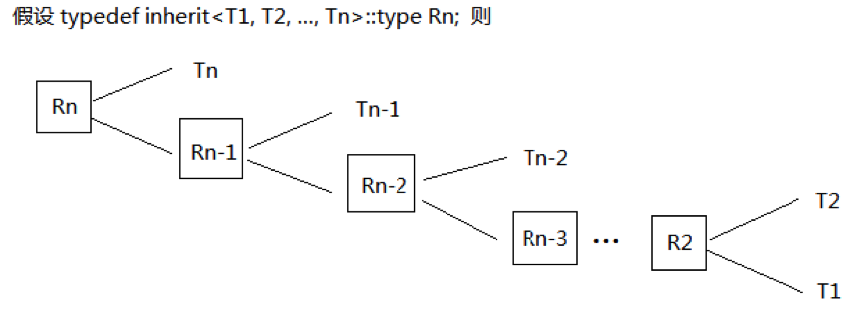
inherit_linearly
template < typename Types , typename Node , typename Root = empty_base > struct inherit_linearly : fold<Types,Root,Node> { };
fold 的一个便于使用的包装器,在基于序列的类合成的上下文中使用。持续调用二元的 Node 函数,以上一次 Node 调用的结果(第一次调用时使用 Root) 以及 前向序列 Types 中的类型为参数。
例如:
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\mpl\inherit.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\vector.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\inherit_linearly.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
using mpl::_1;
using mpl::_2;
template< typename T >
struct tuple_field
{
T field;
};
template< typename T >
inline T& field(tuple_field<T>& t)
{
return t.field;
}
typedef mpl::inherit_linearly<
mpl::vector<int, char const*, bool>
, mpl::inherit< _1, tuple_field<_2> >
>::type tuple;
int main()
{
tuple t;
field<int>(t) = -1;
field<char const*>(t) = "text";
field<bool>(t) = false;
std::cout
<< field<int>(t) << '\n'
<< field<char const*>(t) << '\n'
<< field<bool>(t) << '\n';
return 0;
}
输出:
-1
text
0
说明:
- 注意到实现中,inherit即
fold<Types,Root,Node>,关键是二元操作Node为:inherit< _1, tuple_field<_2> >,这样应用fold迭代的效果,就成了结果R继承自当前的状态S,以及下一个元素的tuple_field<_>类型,最终的结果就是二叉继承体系,继承自多个tuple_field。 - 这个tuple不是完善的,因为依赖于上述的field函数(
T& field(tuple_field<T>& t))获取基类数据的方式,一旦出现相同类型的T,将无法取到。
- numeric_cast
数值转换
- min 与max
比较两个数中的较大与较小值
- sizeof_
算法
MPL 提供了大范围的基础算法,以满足编译期数据序列处理所需的主要操作。这些算法包括有多数STL算法的编译期对应物,以及借鉴函数式编程语言的迭代器算法,等等。
C++标准库中的算法是操作于隐式的迭代器区间之上的,而MPL中的对应物则多数接受并返回序列。这一结果并不是C++编译器计算本身的功能性的要求,而是出于要提高本库的通用性的考虑,使之可以尽可能地用于编译期数据结构的编程。
概念
- 插入器
- 插入器 是STL 输出迭代器 的编译期对应物。实际上,它只是一个持有两个实体的类型:一个状态和一个操作。当被传递给一个转化算法时,将对每个元素调用插入器的二元操作,就象写出到输出迭代器,元素本身被作为第二个参数,而第一个参数为上一次调用的结果或者为插入器的初始状态。技术上,转化算法并不是接受单个插入器参数,而是分别接受一个状态和”输出”操作。不过,将它们组成单个参数,使得算法在语义和语法上更接近STL的对应物,在常见的多数用例中可以得到明显的简化。
- 可逆算法
- 可逆算法是一对以相反顺序对输入序列进行迭代的转化算法中的一个。对于每个可逆算法x都存在一个对应的算法reverse_x,它具有与x相同语义,除了以相反的顺序处理输入序列参数的元素。
插入器
为了更好的灵活性和可用性,MPL算法基本都返回序列(而不是迭代器),因而为方便产生序列,算法还支持额外的模板参数来决定插入器,当然大部分算法都加入了默认的插入器,然而通过配置自己需要的插入器,这也给了算法无限的灵活性,让插入器的迭代变化可以直接应用于每一个算法,如果需要的话。
inserter
template < typename Sequence // 目标序列的基础状态 , typename Operation // 二元操作 op< state, argu > > struct inserter { typedef Sequence state; typedef Operation operation; };
对于任意二元 Lambda 表达式 op 以及任意类型 state: inserter< state ,op > 表示一个插入器,它是插入器的通用model。
#include "print_seq.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\type_traits.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\copy.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\lambda.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\insert.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\range_c.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\vector.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
template< typename N >
struct is_odd
: mpl::bool_< ( N::value % 2 ) >
{};
int main()
{
typedef mpl::if_< is_odd<mpl::_2>, mpl::push_back<mpl::_1, mpl::_2>, mpl::_1 > insert_oper;
typedef mpl::inserter< mpl::vector<>, insert_oper > copy_inserter;
typedef mpl::copy< mpl::range_c<int,0,10>, copy_inserter>::type odds;
print_seq::PrintSequence<odds>();
return 0;
}
打印结果:
1
3
5
7
9
说明:
- 对于insert_oper,占位符表达式,接受两个参数,第一个_1可以是前向序列,_2为序列的元素,并且当第二个参数为奇数的整型常量时,将其插入到第一个参数对应的序列中。
- 对于copy_inserter,其初始状态为空的
mpl::vector<>序列,而二元操作为insert_oper。 copy< range_c<int,0,10>, copy_inserter >::type从空的vector<>空序列开始,针对range_c序列的每个参数,如果是奇数整型常量的,加入到序列中。
- back_inserter
在序列的后端插入元素。
template< typename Seq >
struct back_inserter;
对于任意后端可扩展序列 s,back_inserter<s> 等价于
inserter<s, push_back<_1,_2> >
- front_inserter
在序列的头部插入元素。
template<typename Seq>
struct front_inserter;
对于任意 前端可扩展序列 s,front_inserter<s> 等价于
inserter<s,push_front<_1,_2> >
迭代算法
fold 或 accumulate (两者功能相同)
template < typename Sequence , typename State , typename ForwardOp > struct fold;
持续调用二元 ForwardOp,以上一次调用 ForwardOp 所得结果(第一次调用时使用 State)和区间 [begin<Sequence>::type, end<Sequence>::type) 的每个元素为参数,返回最终的结果。
fold< s, state, op >::type 等价于:
iter_fold< s, state, apply_wrap2< lambda<op>::type, _1, deref<_2> > >::type
对于fold,op的第二个参数为序列的元素;而对于iter_fold,其op的第二个参数为序列迭代器。
例如:
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\mpl\lambda.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\fold.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\iter_fold.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\vector.hpp>
#include <boost\type_traits.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
int main()
{
using mpl::_1;
using mpl::_2;
typedef mpl::vector<long,float,short,double,float,long,long double> types;
typedef mpl::if_< boost::is_float<_2>, mpl::next<_1>, _1 > oper;
typedef mpl::fold< types, mpl::int_<0>, oper >::type number_of_floats;
std::cout << number_of_floats::value << '\n';
// 封装iter_fold的op
typedef mpl::apply_wrap2< mpl::lambda<oper>::type, _1, mpl::deref<_2> > iter_oper;
typedef mpl::iter_fold< types, mpl::int_<0>, iter_oper >::type number_of_floats2;
std::cout << number_of_floats2::value << '\n';
return 0;
}
输出:
4
4
iter_fold
template< typename Sequence , typename State , typename ForwardOp > struct iter_fold;
持续调用二元 ForwardOp,以上一次调用 ForwardOp 所得结果(第一次调用时使用 State)和区间 [begin<Sequence>::type, end<Sequence>::type) 的每个迭代器为参数,返回最终的结果。
reverse_fold
template < typename Sequence , typename State , typename BackwardOp , typename ForwardOp = _1 > struct reverse_fold;
持续调用二元 BackwardOp,以上一次 BackwardOp 调用的结果(第一次调用使用 State)以及区间 [begin<Sequence>::type, end<Sequence>::type) 中反序的每个元素为参数,并返回最终的结果。
如果提供了 ForwardOp, 则它被以前向遍历的方式调用,并将得到的结果传递给第一次的 BackwardOp 调用。即:
typedef reverse_fold< s, state, backward_op, forward_op >::type t; 等价于
typedef reverse_fold< s, fold<s, state, forward_op>::type, backward_op >::type t;
例如(以反向顺序打印序列中除了float的类型):
#include "print_seq.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\mpl\lambda.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\reverse_fold.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\push_back.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\vector.hpp>
#include <boost\type_traits.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
int main()
{
using mpl::_1;
using mpl::_2;
typedef mpl::vector<long,float,short,double,float,long,long double> types;
typedef mpl::reverse_fold<
types,
mpl::vector<>,
mpl::if_< boost::is_same<float, _2>, _1, mpl::push_back<_1, _2 > >
>::type except_float_types;
print_seq::PrintSequence<except_float_types>();
return 0;
}
输出:
long double
long
double
short
long
注意:
必须显示的包含头文件<boost\mpl\push_back.hpp>,因为boost可能对这些固有元函数有默认实现,不包含特定的实现文件,也能编译通过,但是这种情况下是没有意义的。
- reverse_iter_fold
持续调用二元 BackwardOp,以上一次 BackwardOp 调用的结果(第一次调用使用State)以及区间 [begin<Sequence>::type, end<Sequence>::type) 中反序的每个迭代器为参数,并返回最终的结果。如果提供了 ForwardOp, 则以前向遍历的方式调用它,并将得到的结果传递给第一次 BackwardOp 调用。
查询算法
1、find
template< typename Sequence, typename T>
struct find;
返回一个迭代器,指向 Sequence 中的第一个类型 T.
find<s,t>::type 等价于 find_if<s, is_same<_,t> >::type
2、find_if
template
<
typename Sequence
, typename Pred
>
struct find_if;
返回一个迭代器,指向 Sequence 中第一个满足谓词 Pred 的元素。
对于find_if<s,pred>::type,其返回迭代器i满足:
- i 是区间
[begin<s>::type, end<s>::type)中第一个满足apply< pred,deref<i>::type >::type::value == true的迭代器。 - 如果这样的迭代器不存在,i 等同于
end<s>::type.
3、contains
template<typename Sequence, typename T>
struct contains;
返回一个真值 整型常量,如果 Sequence 中有一个或以上元素等同于 T.
contains<s,t>::type 等价于 not_< is_same< find<s,t>::type, end<s>::type> >::type
4、count
template
<
typename Sequence
, typename T
>
struct count;
返回 Sequence 中等同于 T 的元素数量。
5、count_if
template
<
typename Sequence
, typename Pred
>
struct count_if;
返回 Sequence 中满足谓词 Pred 的元素数量。
typedef count_if<s,pred>::type n; 等价于
typedef lambda<pred>::type p;
typedef fold<
s,
long_<0>,
if_< apply_wrap1<p,_2>, next<_1>, _1 >
>::type n;
6、lower_bound
template
<
typename Sequence
, typename T
, typename Pred = less<_1,_2>
>
struct lower_bound;
返回已排序的 Sequence 中第一个可以插入 T 而不破坏顺序性的位置(迭代器)。
与STL中的算法语义类似:第一个大于等于T的位置。
typedef lower_bound< s, x, pred >::type i;
语义:
i 是 [begin<s>::type, end<s>::type) 中满足以下条件的最靠后的迭代器(即最后一个满足的),
对于 [begin<s>::type, i) 中的每个j,apply< pred, deref<j>::type, x >::type::value == true
7、upper_bound
template
<
typename Sequence
, typename T
, typename Pred = less<_1,_2>
>
struct upper_bound;
返回已排序的 Sequence 中最后一个可以插入 T 而不破坏顺序性的位置。
与STL中的算法语义类似:第一个大于T的位置。
typedef upper_bound< s, x, pred >::type i;
语义:
i 是 [begin<s>::type, end<s>::type) 中满足以下条件的最靠后的迭代器,
对于 [begin<s>::type, i) 中的每个j,apply< pred, x, deref<j>::type >::type::value == false
8、min_element
template< typename Sequence, typename Pred = less<_1,_2> >
struct min_element;
返回指向 Sequence 中最小元素的迭代器。
9、max_element
返回指向 Sequence 中最大元素的迭代器。
10、equal
template
<
typename Seq1
, typename Seq2
, typename Pred = is_same<_1,_2>
>
struct equal;
返回一个真值 整型常量 如果两个序列 Seq1 和 Seq2 逐个元素比较时是相同的。
转化算法
copy
template < typename Sequence, // 原序列 typename In = unspecified // 插入器 > struct copy;
返回序列的一个拷贝。
copy<s, in>::type 等价于 fold< s, in::state, in::operation >::type
例如:
typedef vector_c<int,0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9> numbers;
typedef copy<
range_c<int,10,20>
, back_inserter< numbers >
>::type result;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_RELATION( size<result>::value, ==, 20 );
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( equal< result,range_c<int,0,20> > ));
copy_if
template < typename Sequence , typename Pred // 对序列中满足条件的进行插入 , typename In = unspecified > struct copy_if;
返回给定序列中满足某个谓词 Pred 的元素的拷贝。
copy_if<s, pred, in>::type 等价于
typedef lambda<pred>::type p;
typedef lambda<in::operation>::type op;
fold< s , in::state
, eval_if<
apply_wrap1<p,_2>
, apply_wrap2<op,_1,_2>
, identity<_1>
>
>::type
例子:
#include "print_seq.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\mpl\lambda.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\fold.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\push_back.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\vector.hpp>
#include <boost\type_traits.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\inserter.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\apply.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\if.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\identity.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\copy_if.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
int main()
{
using mpl::_1;
using mpl::_2;
typedef mpl::vector<long,float,short,double,float,long,long double> types;
typedef boost::is_float<mpl::_> pred;
typedef mpl::inserter< mpl::vector<>, mpl::push_back<_1, _2> > in;
typedef mpl::copy_if< types, pred, in >::type result1;
print_seq::PrintSequence<result1>();
std::cout << "\n";
// 以下与copy_if等价
typedef mpl::lambda<pred>::type p;
typedef mpl::lambda<in::operation>::type op;
typedef mpl::fold< types , in::state,
mpl::eval_if <
mpl::apply_wrap1<p,_2>
, mpl::apply_wrap2<op,_1,_2>
, mpl::identity<_1>
>
>::type result2;
print_seq::PrintSequence<result2>();
return 0;
}
- transform
它有以下两种操作形式:
template
<
typename Sequence
, typename Op
, typename In = unspecified // 默认是back_inserter
>
struct transform;
transform<Seq,Op > 返回一个原有序列转化后的拷贝,转化的方式是对区间 [begin<Sequence>::type, end<Sequence>::type) 中的每个元素执行单参转化 Op.
typedef transform<s,op,in>::type r; 等价于
typedef lambda<op>::type f;
typedef lambda<in::operation>::type in_op;
typedef fold<
s
, in::state
, bind< in_op, _1, bind<f, _2> >
>::type r;
注意:
转化语义中,插入器inserter的第二个参数要用f先调用下,故绑定为in_op< _1, bind<f, _2> >,再通用的方式,外层也使用bind来绑定封装下:bind< in_op, _1, bind<f, _2> >
template
<
typename Seq1
, typename Seq2
, typename BinaryOp
, typename In = unspecified
>
struct transform;
transform<Seq1,Seq2,Op > 返回一个新的序列,用以下方式生成,对区间 [begin<Seq1>::type, end<Seq1>::type) 和 [begin<Seq2>::type, end<Seq2>::type) 中的元素对 (e1, e21) 执行二元转化 BinaryOp.
typedef transform<s1,s2,op,in>::type r; 等价于
typedef lambda<op2>::type f;
typedef lambda<in::operation>::type in_op;
typedef fold<
pair_view<s1,s2>
, in::state
, bind<
in_op
, _1
, bind<f, bind<first<>,_2>, bind<second<>,_2> >
>
>::type r;
例如:
typedef vector<char,short,int,long,float,double> types;
typedef vector<char*,short*,int*,long*,float*,double*> pointers;
typedef transform< types,boost::add_pointer<_1> >::type result;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( equal<result,pointers> ));
replace
template < typename Sequence , typename OldType , typename NewType , typename In = unspecified > struct replace;
返回原有序列的一个拷贝,将其中每个等同于 OldType 的类型替换为 NewType.
replace<s, x, y, in>::type 等价于 replace_if< s, is_same<_,x>, y, in >::type
replace_if
template < typename Sequence , typename Pred , typename NewType , typename In = unspecified > struct replace_if;
返回原有序列的一个拷贝,其中每个满足谓词 Pred 的类型被替换为 NewType.
typedef replace_if<s, pred, x, in>::type r; 等价于
typedef lambda<pred>::type p;
typedef transform< s, if_< apply_wrap1<p,_1>, x, _1>, in >::type r;
注:包装一个一元op,满足apply_wrap1<p, _1>时选择新的x,否则返回原参数_1
remove
template < typename Sequence , typename T , typename In = unspecified > struct remove;
返回一个新序列,包含区间 [begin<Sequence>::type, end<Sequence>::type) 中除了等同于 T 的元素以外的所有元素。
remove_if
template < typename Sequence , typename Pred , typename In = unspecified > struct remove_if;
返回一个新序列,包含区间 [begin<Sequence>::type, end<Sequence>::type) 中的所有元素,除了满足谓词 Pred 的元素以外。
unique
template < typename Seq , typename Pred , typename In = unspecified > struct unique;
返回一个序列,包含原始序列 Seq 中每个由连续的相同元素组成的子序列中的第一个元素。
partition & stable_partition
template < typename Seq , typename Pred , typename In1 = unspecified , typename In2 = unspecified > struct partition; // 与 stable_partition同义
例如:
template< typename N > struct is_odd : bool_<(N::value % 2)> {};
typedef partition<
range_c<int,0,10>
, is_odd<_1>
, back_inserter< vector<> >
, back_inserter< vector<> >
>::type r;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( equal< r::first, vector_c<int,1,3,5,7,9> > ));
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( equal< r::second, vector_c<int,0,2,4,6,8> > ));
sort
template < typename Seq , typename Pred = less<_1,_2> , typename In = unspecified > struct sort;
返回一个新的序列,将区间 [begin<Seq>::type, end<Seq>::type) 中的所有元素依据顺序关系 Pred 进行排序。
例如:
typedef vector_c<int,3,4,0,-5,8,-1,7> numbers;
typedef vector_c<int,-5,-1,0,3,4,7,8> expected;
typedef sort<numbers>::type result;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( equal< result, expected, equal_to<_,_> > ));
reverse & reverse_copy
template < typename Sequence , typename In = unspecified > struct reverse;
返回原始序列的一个反序的拷贝。reverse 是 reverse_copy 的同义词。
// 以下算法为同名算法的逆序操作,返回相应逆序对应的序列
reverse_copy_if
reverse_transform
reverse_replace
reverse_replace_if
reverse_remove
reverse_remove_if
reverse_unique
reverse_partition
reverse_stable_partition
运行期算法函数 for_each
template
<
typename Sequence
, typename F
>
void for_each( F f );
for_each<Sequence>( f ) 将运行期函数对象 f 应用于区间 [begin<Sequence>::type, end<Sequence>::type) 中的每个元素。
for_each<s>( f ); 等价于
typedef begin<Sequence>::type i1;
value_initialized< deref<i1>::type > x1;
f(boost::get(x1));
typedef next<i1>::type i2;
value_initialized< deref<i2>::type > x2;
f(boost::get(x2));
...
value_initialized< deref<in>::type > xn;
f(boost::get(xn));
typedef next<in>::type last;
说明:
针对每个元素类型,进行value_ initialized计算,value_ initialized提供了对类型初始化的全面支持,保证:内建类型(如int等),按照 T val = T();的方式初始化;类类型以默认构造函数的方式初始化,并且不需要有拷贝构造函数。
例如:
#include <iostream>
#include <boost\mpl\for_each.hpp>
#include <boost\mpl\range_c.hpp>
namespace mpl = boost::mpl;
template<typename T>
struct AccuOp
{
void operator() ( T const& t )
{
if ( t % 2 != 0 )
{
val += t;
}
}
// status
AccuOp() : val( T() ) {}
T val;
};
int main()
{
AccuOp<int> op;
mpl::for_each< mpl::range_c<int, 0, 10> >( boost::ref(op) );
std::cout << op.val << std::endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
25
template
<
typename Sequence
, typename TransformOp
, typename F
>
void for_each( F f );
for_each<Sequence,TransformOp>( f ) 将运行期函数对象 f 应用于对区间 [begin<Sequence>::type, end<Sequence>::type) 中每个元素执行 TransformOp 转化后所得到的结果区间。
数据类型
整型常量
整型常量是一个保存有一个整数类型的编译期数值的类。每个 整型常量 同时也是一个无参 元函数,以它自己本身为返回值。整型常量 object 可以隐式转换为对应整数类型的运行期数值。
| 表达式 | 语义 |
|---|---|
n::tag |
n 的标签类型;n::tag::value 为 n 的转换秩(conversion rank) |
n::value_type |
n::value 的一个无cv限定的类型 |
n::value |
所包装的整型常量的值 |
n::type |
is_same<n::type,n>::value == true |
next<n>::type |
类型为 n::value_type 的一个 整型常量 c,满足 c::value == n::value + 1 |
prior<n>::type |
类型为 n::value_type 的一个 整型常量 c,满足 c::value == n::value - 1 |
n::value_type const c = n() |
c == n::value |
模型:
- int_
- long_
- size_t
- char_
bool_
integral_c
template< typename T, T N > struct integral_c;
通用的整型常量的包装器。
杂项
1、pair
template
<
typename T1
, typename T2
>
struct pair
{
typedef pair type;
typedef T1 first;
typedef T2 second;
};
例如: 计算某个序列中的元素数量,并同时计算其中的负数元素数量。
typedef fold<
vector_c<int,-1,0,5,-7,-2,4,5,7>
, pair< int_<0>, int_<0> >
, pair<
next< first<_1> >
, if_<
less< _2, int_<0> >
, next< second<_1> >
, second<_1>
>
>
>::type p;
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_RELATION( p::first::value, ==, 8 );
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_RELATION( p::second::value, ==, 3 );
2、empty_base
struct empty_base {};
3、void_
struct void_
{
typedef void_ type;
};
void_ 是一个表示 “nothing” 的通用类型占位符。
宏
1、静态断言
MPL 提供了一组静态断言宏,它们被设计为针对各个编译器的诊断能力,生成尽可能有用和带有尽量多信息的错误信息。所有断言宏都可以用在类域、函数域或名字空间域。
- BOOST_MPL_ASSERT
对于任意布尔无参 元函数 pred: BOOST_MPL_ASSERT(( pred )); 生成一个编译错误,如果 pred::type::value != true, 否则没有作用。注意,即使条件中没有逗号也要求使用两重括号。
- BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_MSG
对于任意整型常量表达式 expr, 合法 C++ 标识符 message, 以及任意类型 t1, t2,… tn:
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_MSG( expr, message, (t1, t2,... tn) );
生成一个编译错误,如果 expr::value != true, 否则没有作用。如果编译器的诊断能力可以支持,错误信息将包含 message 标识符以及 t1, t2,… tn 类型的列表,
例如:
template< typename T > struct my
{
// ...
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_MSG(
is_integral<T>::value
, NON_INTEGRAL_TYPES_ARE_NOT_ALLOWED
, (T)
);
};
my<void*> test;
- BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_NOT
对于任意无参 元函数 pred:
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_NOT(( pred ));
生成一个编译错误,如果 pred::type::value != false, 否则没有作用。注意要求使用两重括号。
- BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_RELATION
对于任意整型常量 x, y 以及一个合法的 C++ 操作符 op:
BOOST_MPL_ASSERT_RELATION( x, op, y );
生成一个编译错误,如果 ( x op y ) != true, 否则没有作用。
2、内省
- BOOST_MPL_HAS_XXX_TRAIT_DEF
对于任意的合法 C++ 标识符 name:
BOOST_MPL_HAS_XXX_TRAIT_DEF(name)
扩展为一个布尔无参 元函数 has_name 的定义,使得对于任意类型 x:has_name<x>::value == true当且仅当 x 是一个类类型,且具有一个内嵌类型成员 x::name.
